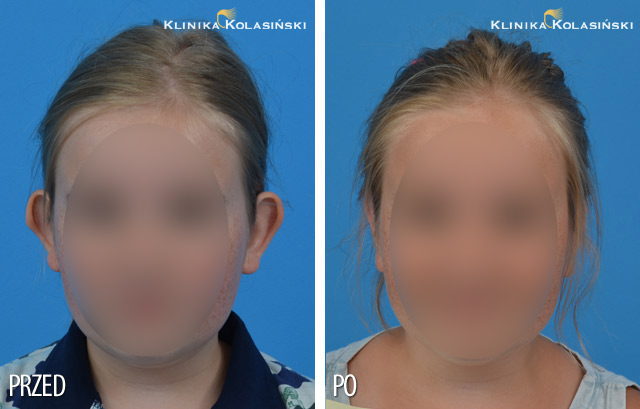
Ear surgery, or otoplasty, is usually done to set prominent ears back closer to the head. It is one of the most frequently performed aesthetic surgeries in the case of children. The protruding ear auricles are the concern of about 5 % of the population. The defect is usually bilateral rarely unilateral and it occurs more often at the female sex.
For the most part, the operation is done on children between the ages of seven and fourteen. Ears are almost fully grow by age seven, and the earlier the surgery, the less teasing and ridicule the child will have to endure. Ear surgery on adults is also possible, and there are generally no additional risks associated with ear surgery on an older patient.
If you′re considering ear surgery for yourself or your child, this information will give you a basic understanding of the procedure – when it can help, how it′s performed, and what results you can expect. It can′t answer all of your questions, since a lot depends on your individual circumstances. Please be sure to ask our doctor if there is anything you don′t understand about the procedure.
Complications and risks
When ear surgery is performed by a qualified, experienced surgeon, complications are infrequent and usually minor. Nevertheless, as with any operation, there are risks associated with and specific complications associated with this procedure.
A small percentage of patients may develop a blood clot on the ear. It may dissolve naturally or can be drawn out with a needle.
Occasionally, patients develop an infection in the cartilage, which can cause scar tissue to form. Such infections are usually treated with antibiotics; rarely, surgery may be required to drain the infected area.
Indications
Most surgeons recommend that parents stay alert to their child′s feelings about protruding ears; don′t insist on the surgery until your child wants the change. Children who feel uncomfortable about their ears and want the surgery are generally more cooperative during the process and happier with the outcome.
In the initial meeting, our surgeon will evaluate your child′s condition, or yours if you are considering surgery for yourself, and recommend the most effective technique. He or she will also give you specific instructions on how to prepare for surgery.
Ear correction
Ear surgery is usually performed as an outpatient procedure in our clinic. Occasionally, our doctor may recommend that the procedure be done as an inpatient procedure, in which case you can plan on staying overnight in the clinic.
Anesthesia
If your child is young, our surgeon may recommend general anesthesia, so the child will sleep through the operation. For older children or adults, the surgeon may prefer to use local anesthesia, combined with a sedative, so you or your child will be awake but relaxed.
The surgery
Ear surgery usually takes about one hour and a half, although more complicated procedures may take longer. The technique will depend on the problem. The surgeon makes a small incision in the back of the ear to expose the ear cartilage. He or she will then sculpt the cartilage and bend it back toward the head. Non-removable stitches may be used to help maintain the new shape. Occasionally, the surgeon will remove a larger piece of cartilage to provide a more natural-looking fold when the surgery is complete. Another technique involves a similar incision in the back of the ear. Skin is removed and stitches are used to fold the cartilage back on itself to reshape the ear without removing cartilage.
In most cases, ear surgery will leave a faint scar in the back of the ear that will fade with time.
Recovery time
Adults and children are usually up and around within a few hours of surgery, although you may prefer to stay overnight in the clinic with a child until all the effects of general anesthesia wear off.
The patient′s head will be wrapped in a bandage immediately following surgery with antibiotics ointment, to promote the best molding and healing. Just before and three days after the surgery, antibiotics are taken orally. The ears may throb or ache a little for a few days, but this can relieved by medication. One week the patient cannot wash his or her hair and it is recommended to refrain from any school, professional and social life. Winter or summer vacations are the best moments to undergo the corrective surgery in the case of children.
Within seven days, the bulky bandage will be taken off and stitches will be removed in the clinic. The ears can be a little swollen and red. However these symptoms disappear after two or three days. Then our surgeon recommend a special headband, especially at nights.
Any activity in which the ear might be bent should be avoided for two months. Most adults can go back to work about seven days after surgery. Children can go back to school after seven days or so, if they′re careful about playground activity. You may want to ask your child′s teacher to keep an eye on the child for a few weeks. The cartilage rebuilts itself within the period of two to six months. After such a period of time becomes hard, elastic and resistant to damages.
Sometimes, however, the correction can leave a scar that′s worse than the original problem. Ask our surgeon about the effectiveness of surgery for your specific case.
Expectations
Most patients, young and old alike, are thrilled with the results of ear surgery. But keep in mind, the goal is improvement, not perfection. Don′t expect both ears to match perfectly-perfect symmetry is both unlikely and unnatural in ears. If you′ve discussed the procedure and your expectations with the surgeon before the operation, chances are, you will be quite pleased with the result.
